|
FQL v4 will be decommissioned on June 30, 2025. Ensure that you complete your migration from FQL v4 to FQL v10 by that date. For more details, review the migration guide. Contact support@fauna.com with any questions. |
Dashboard quick start
This quick start uses the Fauna Dashboard.
-
Sign up at https://dashboard.fauna.com/register.
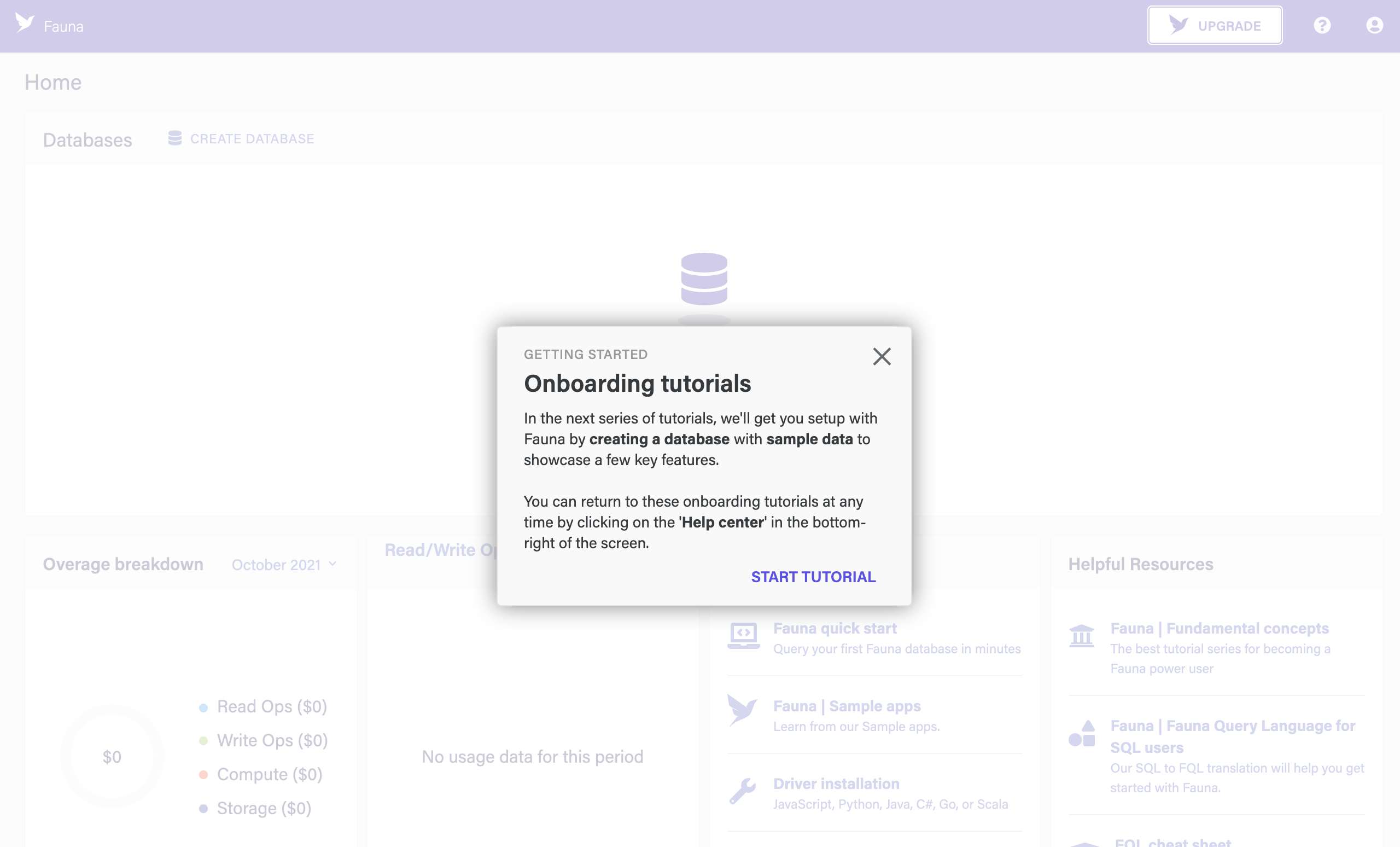
When you first log in, you are greeted with an onboarding tutorial. Click the X button to close it. You can return to the tutorial at any time by clicking the question mark ? button at the bottom right.
-
-
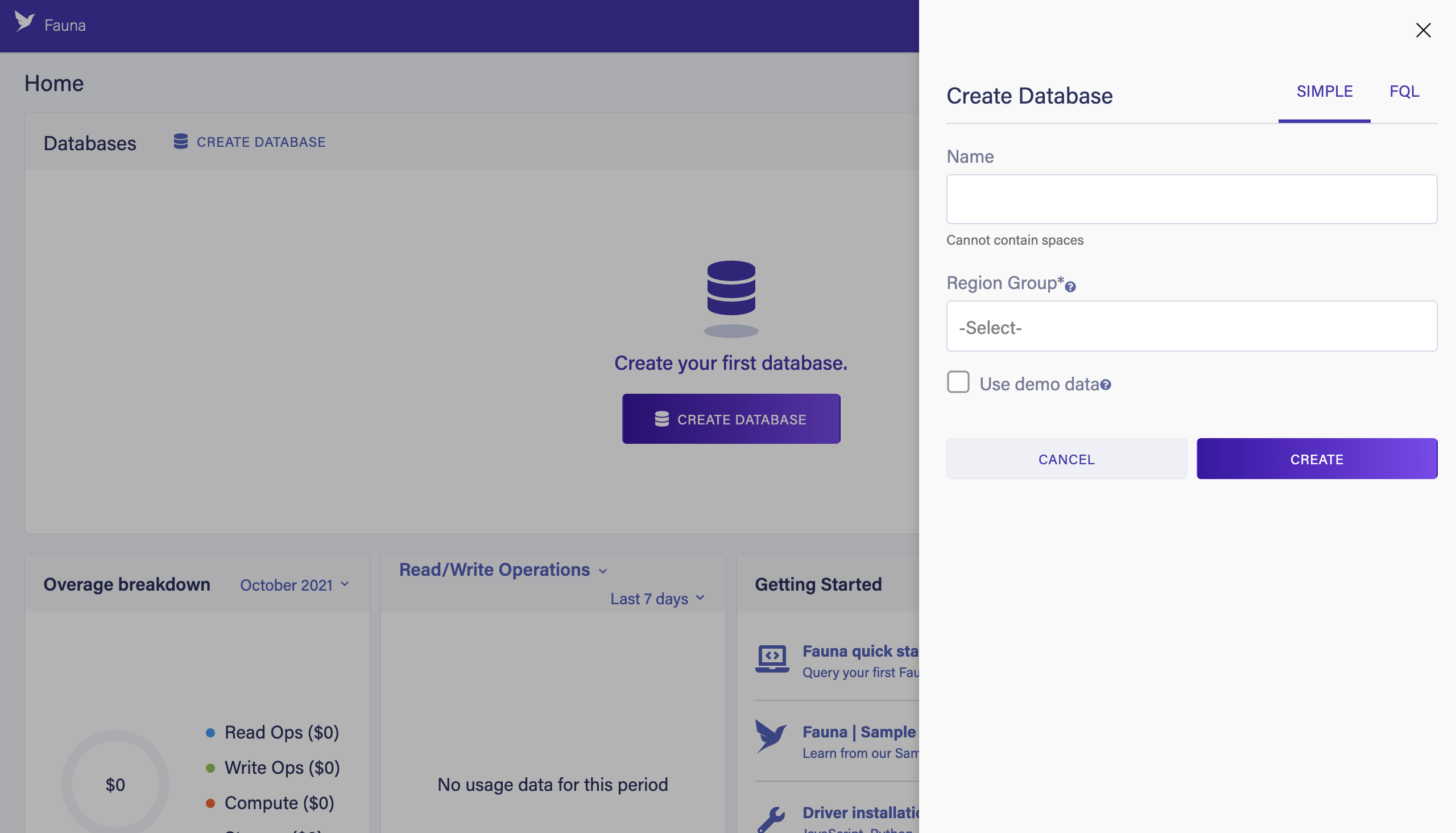
Click CREATE DATABASE.
-
Enter
my_dbinto the "Name" field. -
Select your Region Group from the Region Groups menu.
-
Check the "Use demo data" checkbox.
-
Click CREATE.
You have created your first Fauna database!
-
-
The Overview page for the
my_dbdatabase is displayed. The database has been populated with some collections and indexes for a grocery delivery app.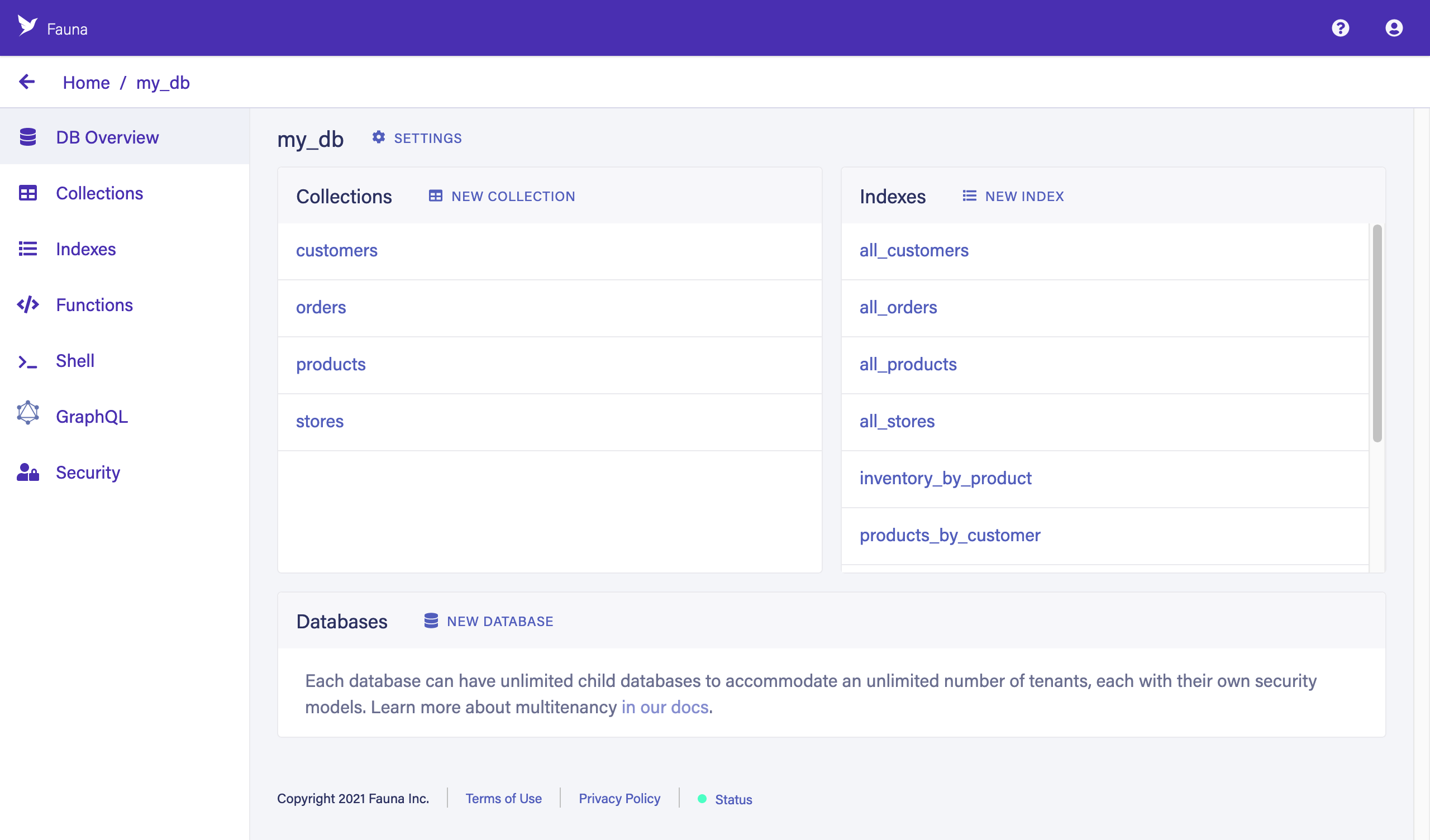
-
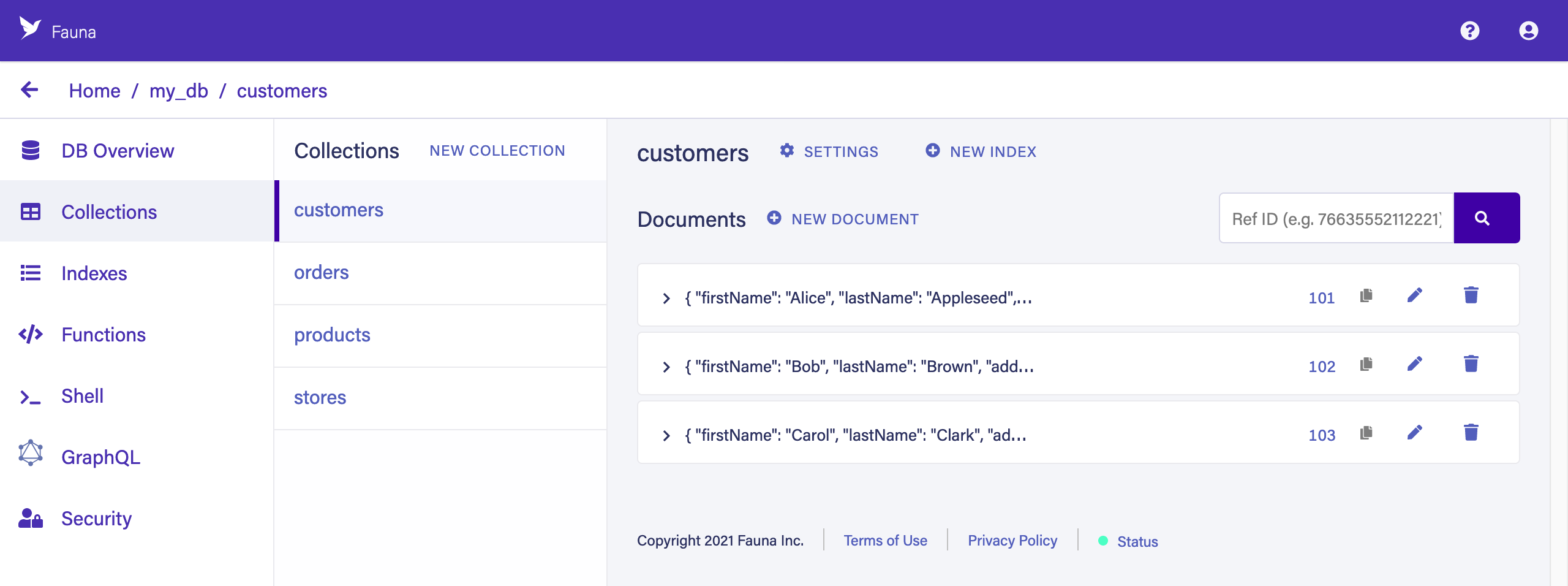
Collections
Click COLLECTIONS in the left sidebar to browse your collections. You’ll see the documents for each collection on the right. If you are familiar with SQL, collections are like tables and documents are like rows in a table, except that each document can contain its own, distinct fields.
-
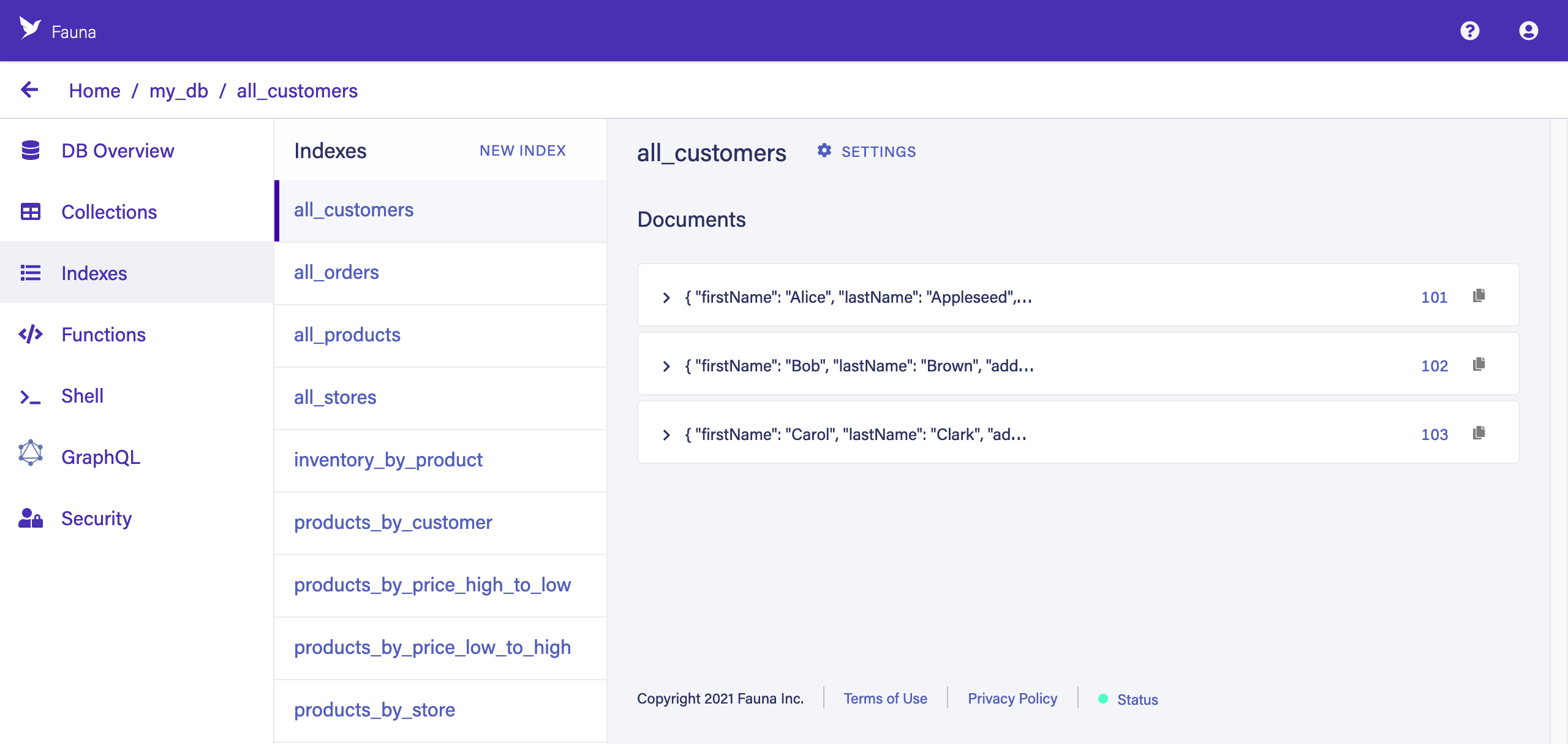
Indexes
Fauna’s query model relies on indexes to support all query patterns which do not involve looking up documents directly by their Reference. An understanding of index creation and usage is crucial for effective Fauna development.
Click the INDEXES tab in the left sidebar. If you are familiar with SQL, Fauna’s indexes are like SQL views. Most Fauna queries require a companion index to help avoid performing full scans of collections (which could get expensive), but you can have hundreds of indexes without affecting overall performance.
-
Functions
Click the FUNCTIONS tab in the left sidebar. User-defined functions (UDFs) contain custom business logic that runs on the server, similar to "stored procedures".
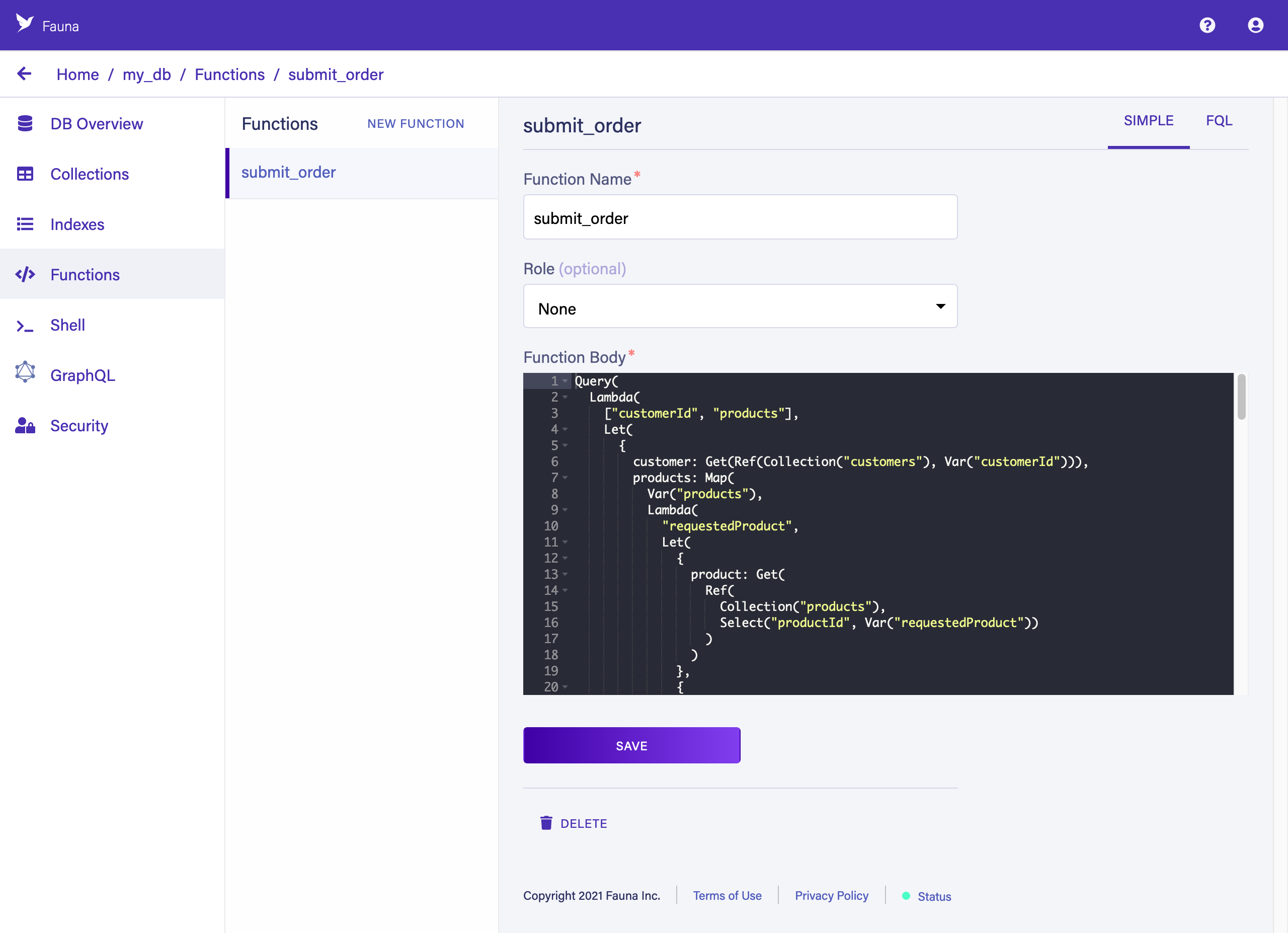
This UDF might look weird if it’s your first time seeing FQL, the FQL, but FQL is actually pretty easy and tons of fun to learn. FQL is also unique in how much power and precision it gives you with respect to predictable cost and performance as you scale.
-
-
Now that we know some basic concepts, let’s query our data.
-
Click on SHELL in the left sidebar to open the web shell.
-
Copy the following FQL query:
Get(Ref(Collection("products"),"202")) -
Replace the queries in the bottom panel of the shell by selecting them and then and pasting the copied query.
-
Click RUN QUERY.
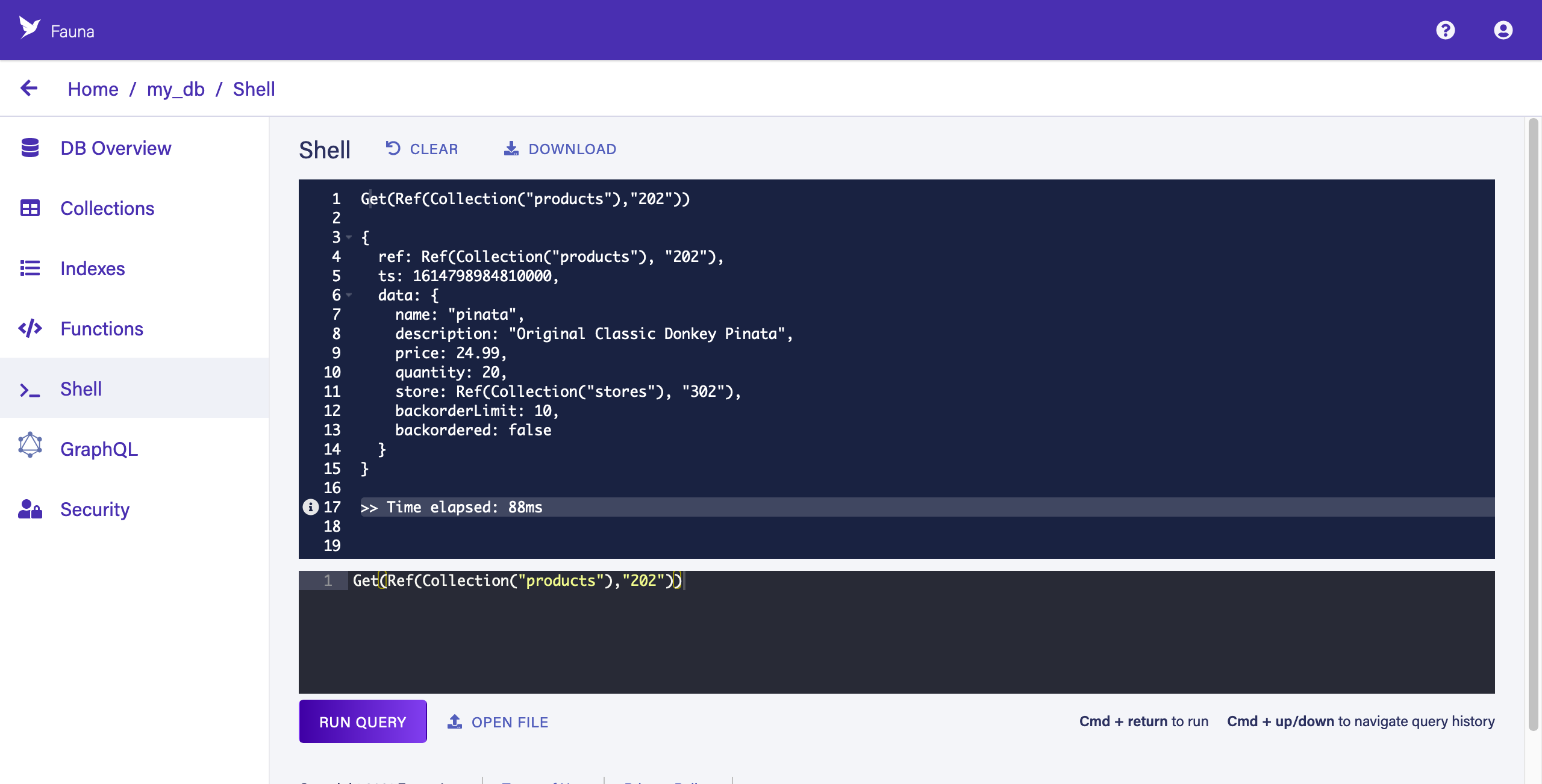
This query simply gets a document identified by its Reference. A document Reference contains a reference to the document’s collection (in this case, "products") and a unique ID for the document in that collection (in this case, "202"). Fauna’s auto-generated Reference IDs are 18-digits long — you can set your own during document creation, as we have done with the pre-populated demo data to ease copy/pasting.
The upper panel contains the result of the query:
-
Hover your pointer over the i icon to the left of "Time elapsed" to see the query execution metrics. For example, here we can learn that this query resulted in one read operation.
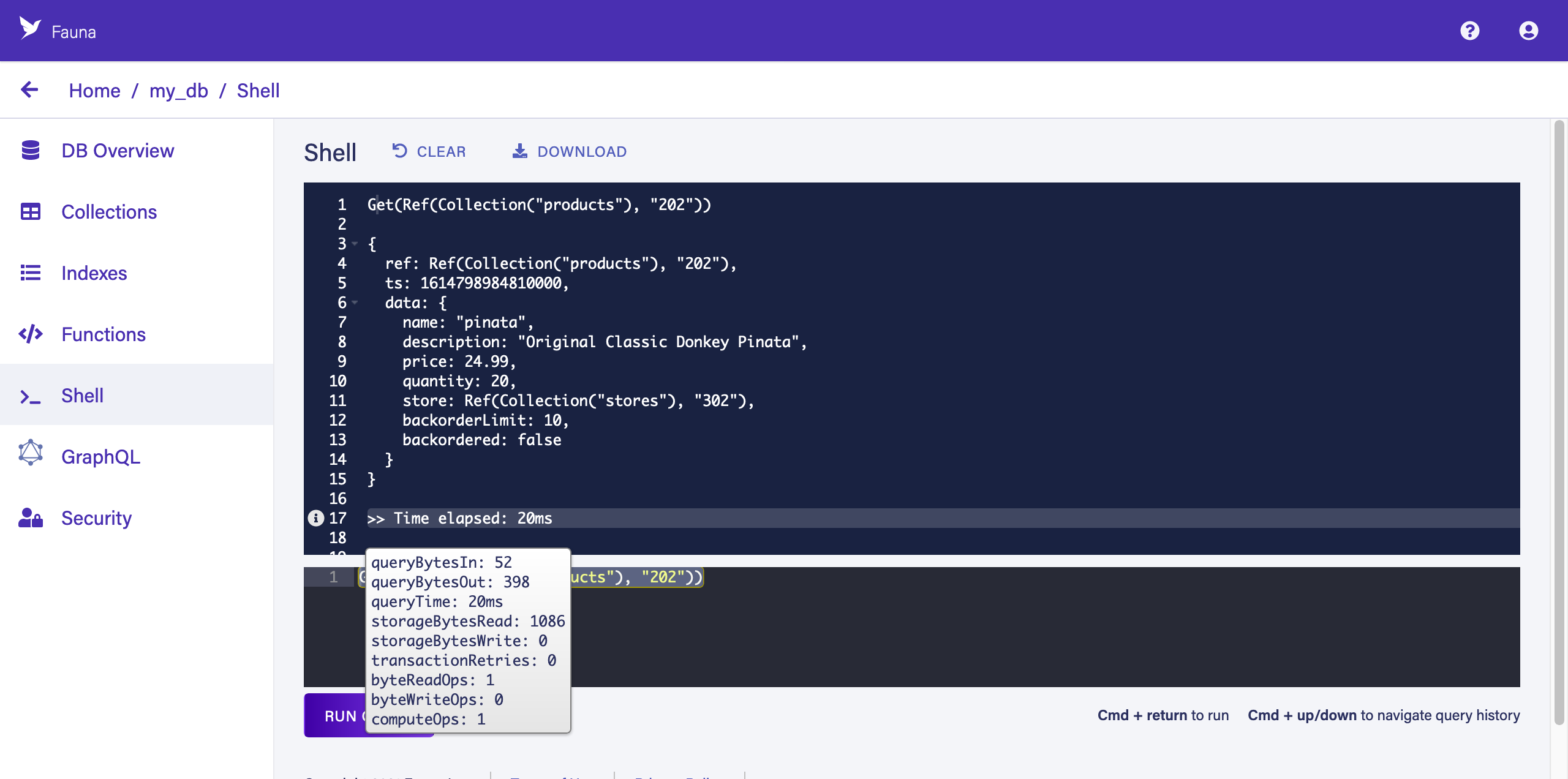
You can reduce read operations by leveraging indexes and using them as views. Expand the following block to learn more.
-
Is this article helpful?
Tell Fauna how the article can be improved:
Visit Fauna's forums
or email docs@fauna.com
Thank you for your feedback!